SIM, Device & Connectivity
Can SIM for Things connect to my RADIUS server?
Yes, SIM for Things packet gateway (PGW) can connect to external RADIUS servers to support most of the Key Authentication, Authorization & Accounting (AAA) procedures.
Supported RADIUS services
Is it recommended to prioritize a specific Radio Access Type (RAT)?
Even though several IoT devices available in the market support multiple Radio Access Types (RAT), it is always suggested to set the right priority sequence and the different RAT for an optimized network search.
To configure your IoT device with AT commands check How to force device to attach to LTE (CAT-M) network as preference?
My device creates dual sessions, how will the quota allocation work with my device?
When a device requests two simultaneous sessions from the the SIM for Things platform, then the platform allows two distinct sessions and reserves 5MB of quota for each session. While the platform reserves 5MB of data, it also has to deduct this from the balance/monthly limit of the endpoint for accurate rating/charging.
5MB * 2 = 10MB Reserved
This reserved volume of data is already deducted from the available monthly limit. If one of the sessions exhausts its allocated 5MB data and requests an additional 5MB of data then the SIM for Things platform will allocate based on the remaining monthly limit, if the monthly limit is reached it will refuse and give a low balance notification. Though the 2nd session will still have its 5MB allocated volume of data not fully exhausted.
Monthly Data Limit/Balance - 10MB
First Data session - 5MB reserved
Second Datasession - 5MB reserved
....
First Data Session - 5MB consumed - Re-request for reservation
Session Data session - 0MB consumed - 5MB reserved
Low Balance as 0MB of balance remainingNow the second 5MB is in the hands of the device and it’s the device only who can decide to consume data or end the session and release the reservation. If the device consumes the second 5MB, the platform doesn’t have to do anything as it has already deducted that from the monthly limit/balance, but if the device decides to release the session and return back some of the unused reservation (for example it uses 2 MB and returns 3MB), the platform will increase the already deducted monthly limit/balance by 3MB, and this 3MB will become available for the endpoint to use in additional sessions. If any additional sessions is requested for the endpoint then 3MB can still be allocated to that session before a low balance notification is given.
Thus, consumption or return of the second session’s 5MB is in hands of the device and only device can decide what to do with it.
The session can also be closed by the platform based on session timers but usually these timers are quite long (e.g. 30 mins to 24 hours).
My SIM-card doesn't connect, how can I fix it?
Diagnosing a SIM card is a several step process, please try the steps below to find a solution:
Go to the
Endpointtab and confirm that your SIM card is linked to anActive Endpoint.Also check if the required services are not barred, as depicted below.
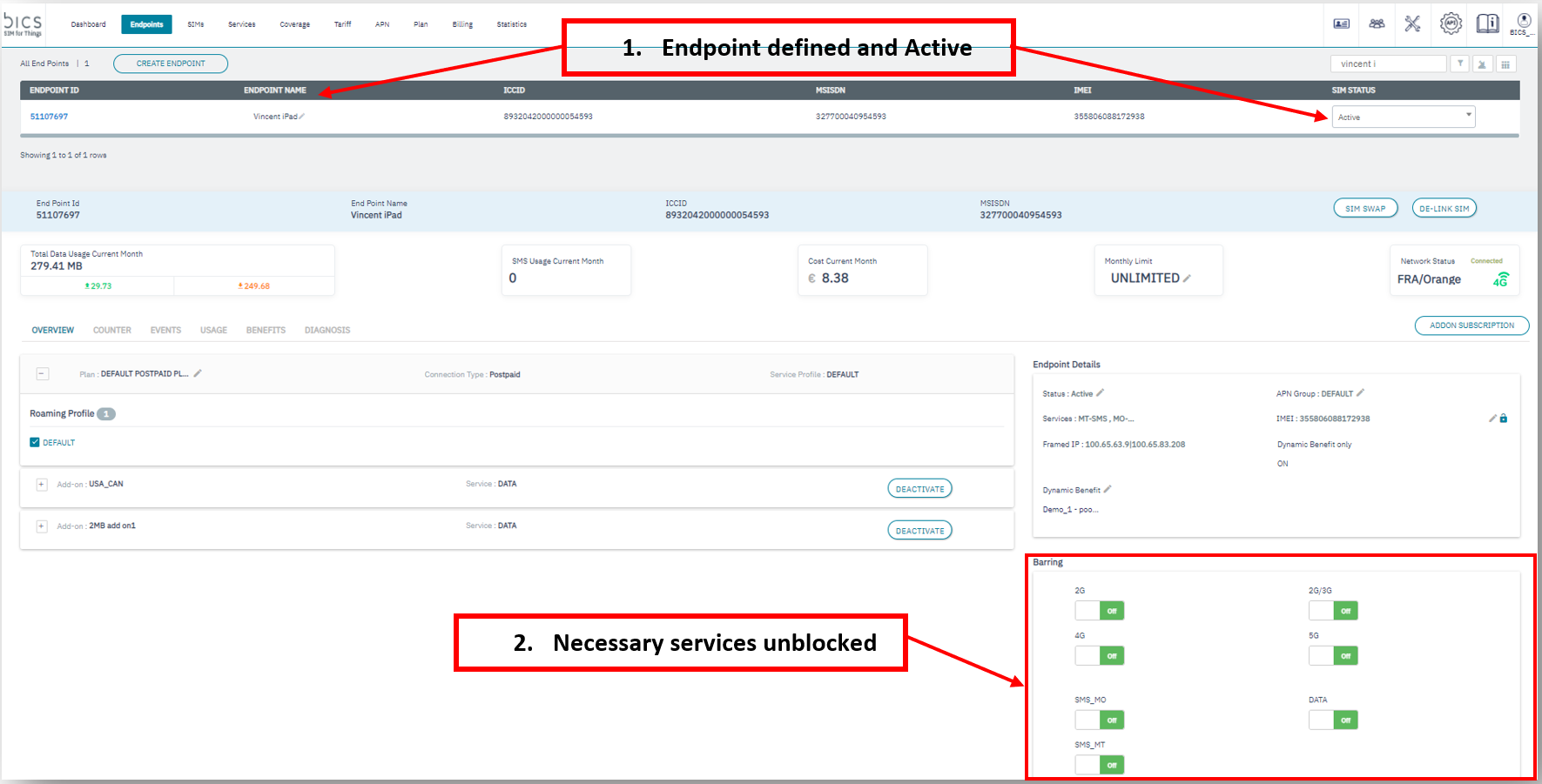
Endpoint CRM
Verify the APN is configured in the device and check if it is one of the allowed APNs in the
APN Group, as depicted below.
After an APN configuration change on the device, make sure to reboot the device so that the new settings are applied.
Some roaming networks may send incorrect
IMEIdata, to diagnose the problem make sure to unlock the “IMEI check” feature, as depicted below.
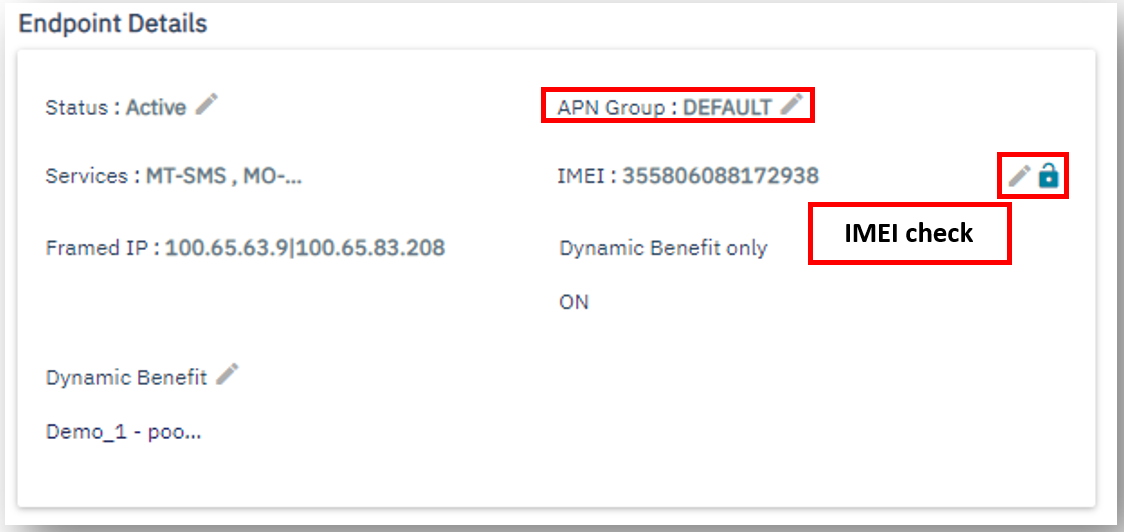
Endpoint Details
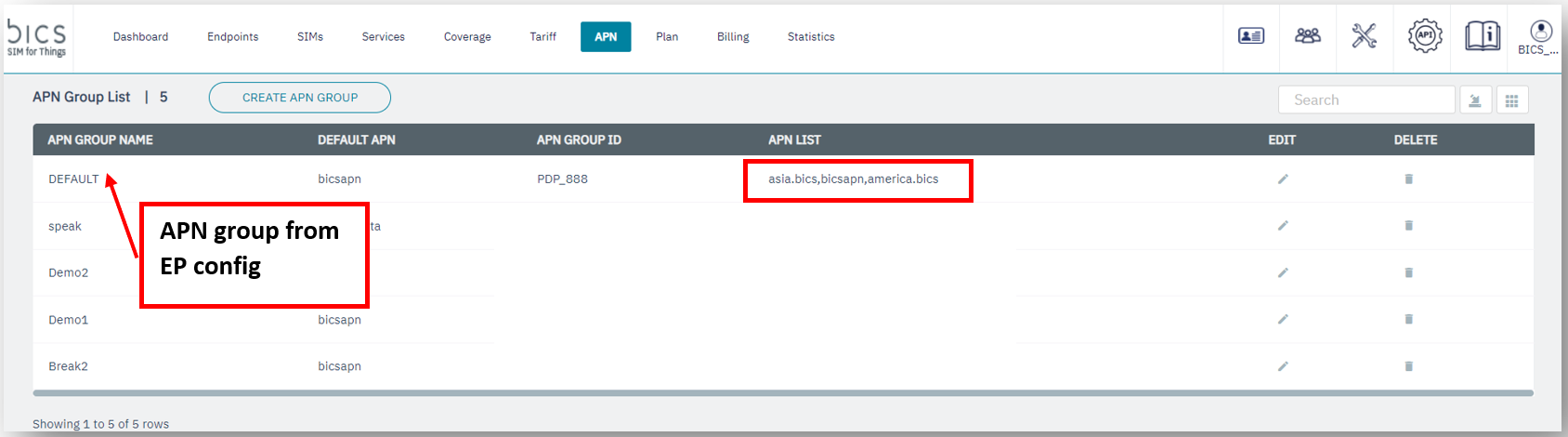
APN Group
To diagnose further – use the
Events,UsageandDiagnosissub-menus for the endpoint.
Detailed information for the logs under the Events and Usage tabs can be found via the View button.
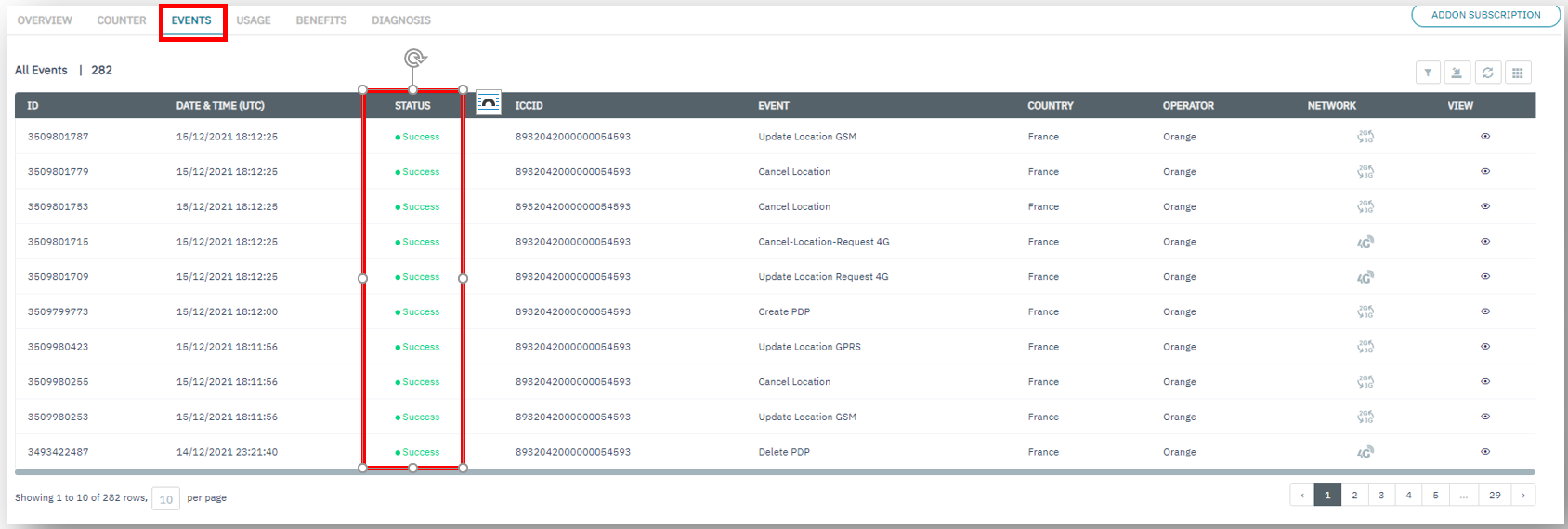
Endpoint Events
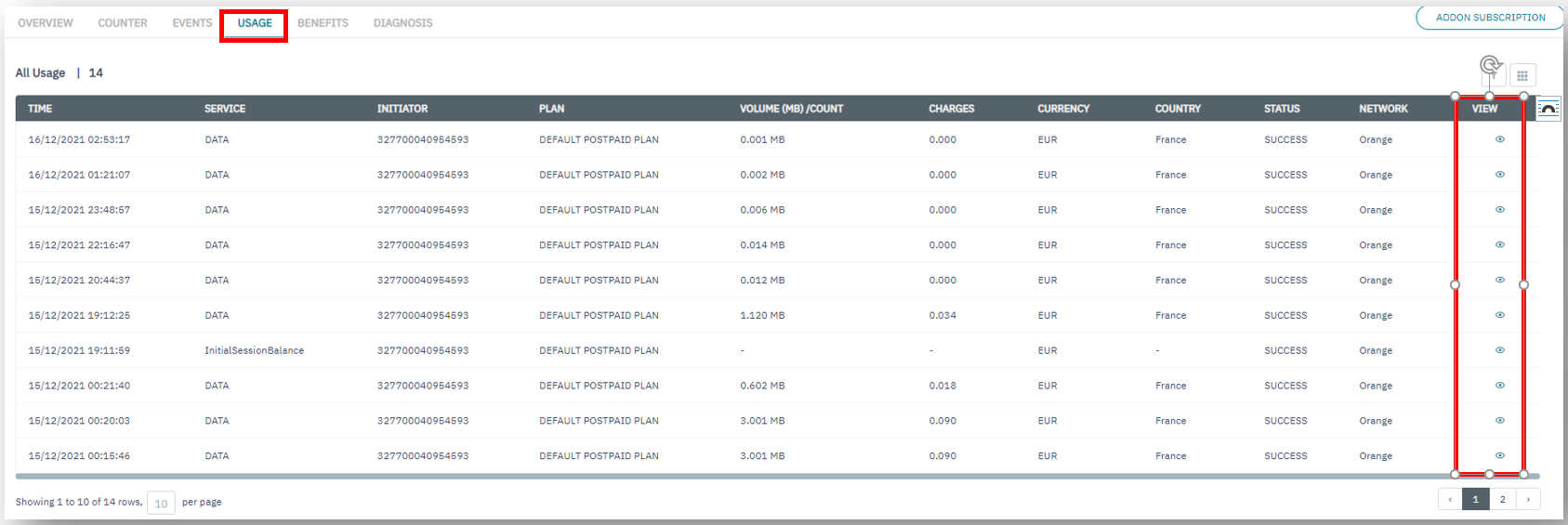
Endpoint Usage
Make sure that visited network is listed in the view network coverage for the endpoint.
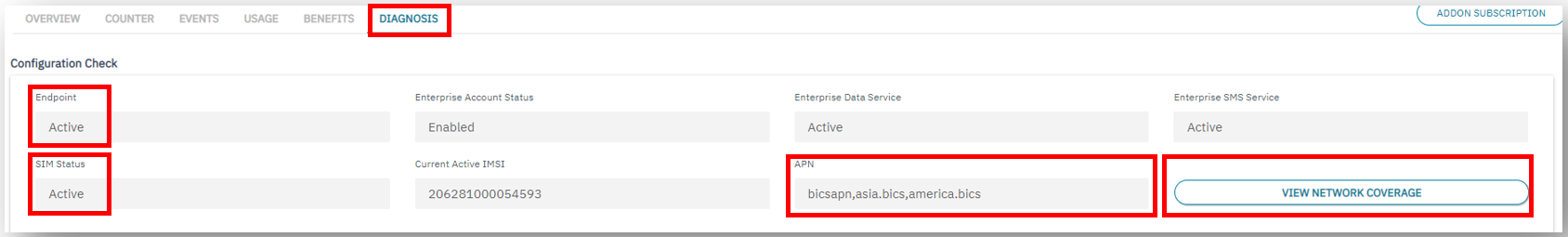
Endpoint Diagnosis
Also validate that the visited network is allowed in the Roaming Profile and a Tariff is defined for that network under the Tariff tab.
What are the different SIM states and how does SIM life-cycle work?
In the SIM for Things platform an endpoint represents a real world customer device https://docs.sft.bics.com/sft/what-is-an-endpoint-and-why-do-i-need-to-create-on , a SIM is used as a connectivity module for this endpoint and can be linked or de-linked from an endpoint as per the need.
Thus the state of a SIM is controlled by the endpoint to which the SIM is linked at a particular moment. Below is a list of possible endpoint and SIM states.
ENDPOINT STATES
Pre-Active
Active
Suspended
Hold
SIM STATES
Ready to Activate
Pre-Active
Active
Suspended
Endpoint & SIM Lifecycle
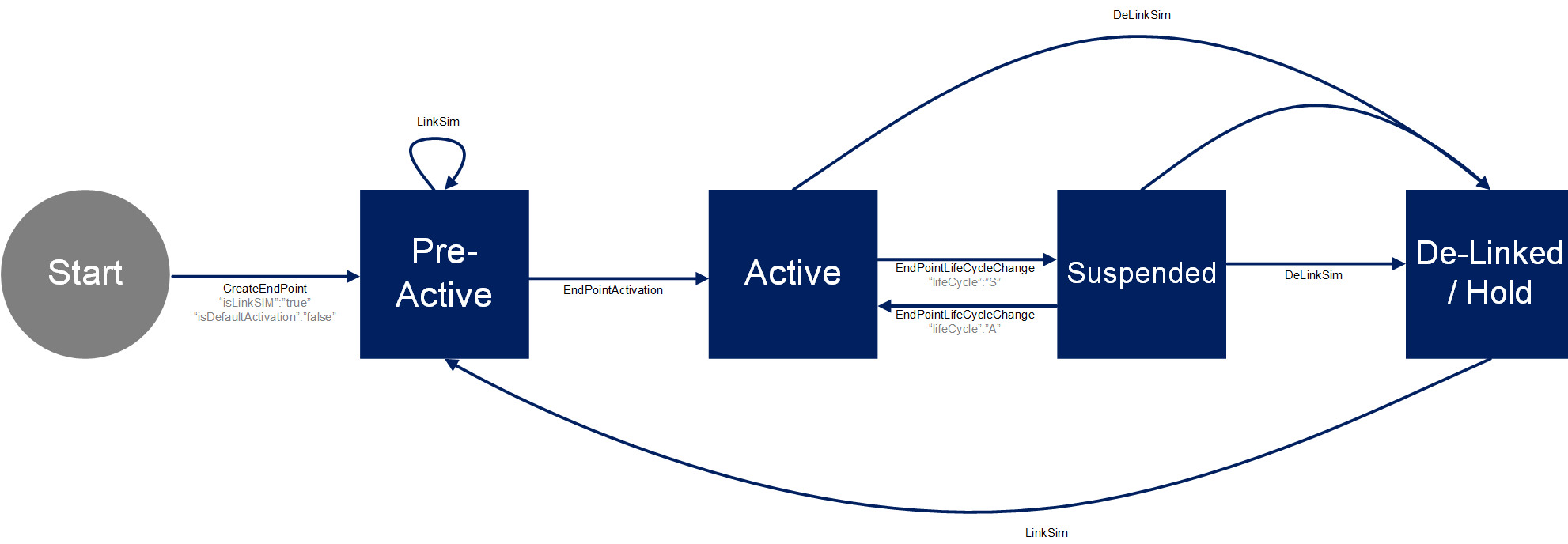
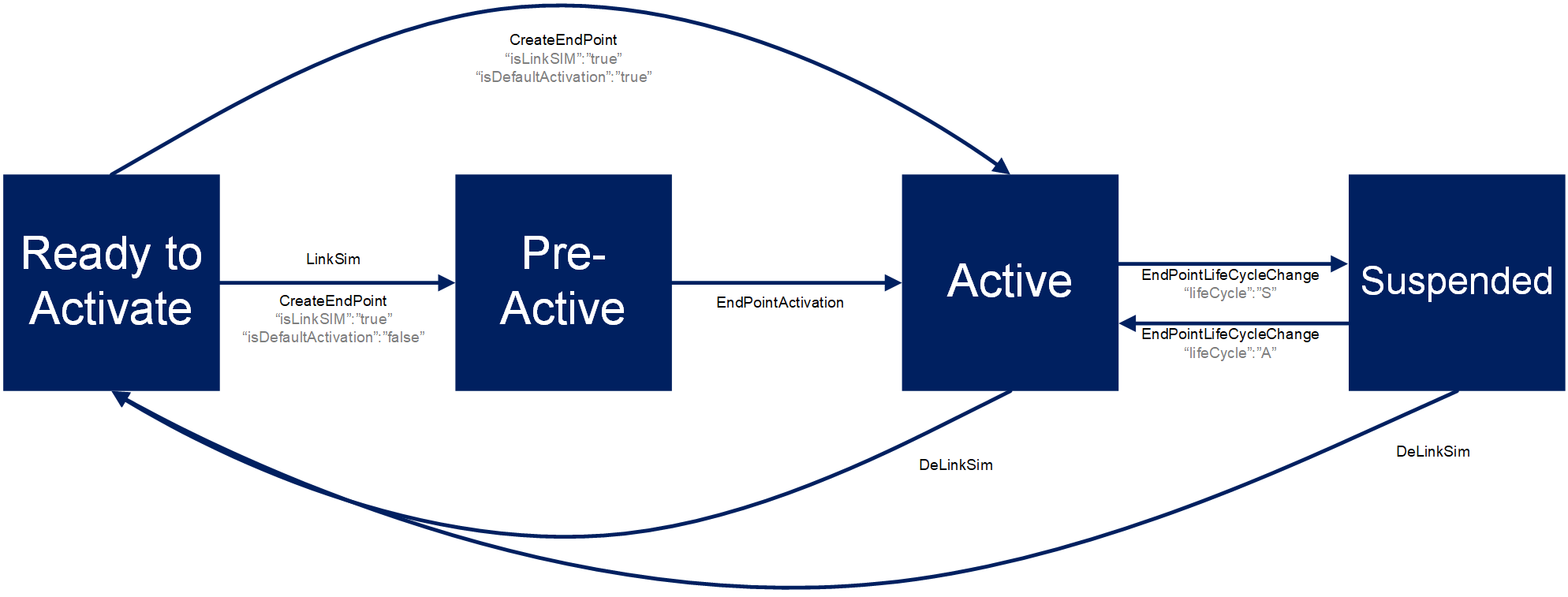
Newly manufactured and delivered SIMs are always in Ready to Activate state. When a new endpoint is created then initially it will be in Pre-Active state.
A SIM can be linked to an endpoint during the creation step itself, then a SIM will also move to Pre-Active state. The SIM is linked to an endpoint but still not active yet. Thus the SIM will not connect to the network if it’s plugged into a device.
When an endpoint is activated then both the endpoint & the associated SIM will move to Active state.
A SIM will work when plugged into a device and inherit the parameters of the plan (coverage, counters, etc.) of the associated endpoint.
It is possible to create an endpoint, link a SIM and activate the endpoint in one single operation either by portal or by API
https://sft.bics.com/api/CreateEndPoint
Activation of an endpoint could be a charged event based on the contract and may accrue SIM activation fees
It is possible to temporarily disable the endpoint and with it the linked SIM by moving to Suspend state – the SIM will not work if it’s plugged into a device. The Endpoint and with it the linked SIM can be switched back to Active state.
Delinking a SIM will move an endpoint into Hold state and a SIM card to Ready to Activate state, returning it to the SIM inventory. The SIM card then be re-used with an existing for newly create endpoints.
As depicted in the below diagrams, endpoint and SIM life-cycle merge upon LinkSim operation and they share the Pre-Active, Active and Suspended states until DeLinkSim operation bring the endpoint to Hold and SIM to Ready to Activate state.
Endpoint State Lifecycle
SIM State Lifecycle
What is an APN and how does it work?
APN (or Access Point Name) is an identifier which allows a user to establish a connection between a local network and the public internet. The local network uses the APN to generate an IP address, define the service type which is required and assign the appropriate security settings.
APNs can also have custom names, which makes them easier to enter and remember. This is especially helpful in cellular IoT applications, where manufacturers have to manually set their APNs in the device settings.
SIM for Things APN support
BICS have three APNs available via default bicsapn, america.bics & asia.bics, which allow access to public internet via local breakout in different regions Europe, North America & Asia respectively.
SIM for Things does provide support for custom private APNs, if you need to use a custom APN, please contact your BICS account manager.
What is the SIM-Swap operation and where has my old SIM gone?
The operation SIM-Swap allows a user to link a new SIM card in Ready to Activate state to an existing endpoint which already has a SIM linked to it.
The operation replaces the ‘old’ SIM with a ‘new’ SIM but keeps all the existing properties of the endpoint (MSISDN, coverage, consumption, balance,…).
The ‘old’ SIM will be removed from the inventory and will no longer be usable. This operation needs to be used carefully but allows a user the possibility to replace a defective or lost SIM for a device.
The existing endpoint can be in Active or Suspended state for the operation SIM-Swap to work. To know more about endpoints and SIM states, check https://docs.sft.bics.com/sft/sim-device-connectivity#SIM,Device&Connectivity-WhatarethedifferentSIMstatesandhowdoesSIMlife-cyclework?
